From vehicles to lawnmowers, internal combustion engines are crucial to many contemporary devices. The 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines are two of the most popular varieties of internal combustion engines. Although both kinds of engines transform fuel into energy, they do so in very different ways mechanically. When it comes to 2 stroke vs 4 stroke engines, both of them include pros and cons.
The fundamental distinctions between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines will be covered in this article.
-
Number of strokes
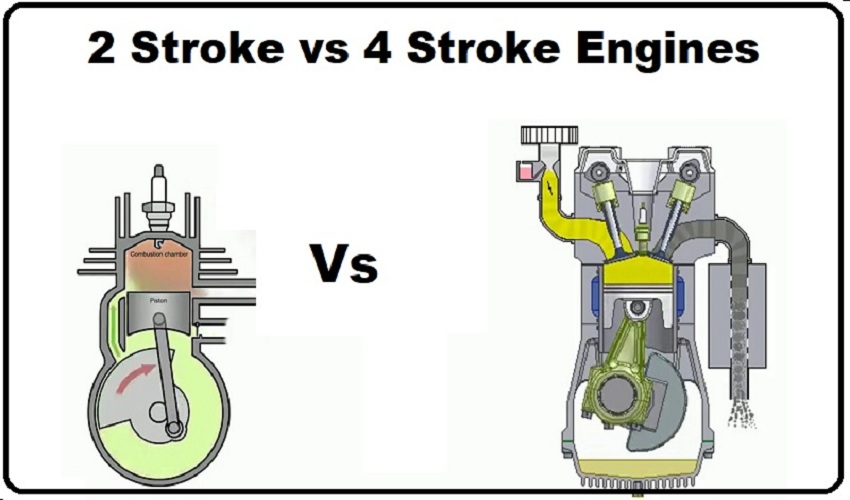
The stroke numbers necessary to complete a combustion cycle are the primary distinction between the two types of engines. The name of the engines is self-explanatory. The compression and the power stroke are the two strokes that make up a 2-stroke engine’s combustion cycle. In contrast, the combustion cycle in a 4-stroke engine is completed by four strokes: the intake, the compression, the power, and the exhaust.
-
Simplicity
Due to its simplicity, a 2-stroke engine is typically lighter, smaller, and less expensive to produce than a 4-stroke engine. Because of this, 2-stroke engines are widely used in products where weight and size are important considerations, such as chainsaws, mopeds, and some small boats. However, 2-stroke engines often use more fuel and pollute more than 4-stroke engines.
-
Fuel Efficiency
Regarding fuel efficiency in 2stroke vs 4stroke engines, 4-stroke outperforms its counterpart. The way 2-stroke engines deliver fuel to the combustion chamber contributes to their decreased fuel economy and more significant emissions. A 2-stroke engine’s combustion chamber receives the gasoline and oil mixture through ports in the cylinder wall. The emission of unburned fuel and contaminants can occur as a result of this process’ potential for incomplete combustion.
On the other hand, the moving elements of 4-stroke engines are lubricated by a separate oil system, which enables a cleaner combustion process. A 4-stroke engine’s intake stroke enables a more thorough mixing of fuel and air, which enhances the combustion process and increases fuel economy.
-
Maintenance Frequency
The need for maintenance is another significant distinction between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. Due to their straightforward construction and requirement to mix oil and gasoline, 2-stroke engines need maintenance more frequently. Throughout the engine’s lifetime, this may lead to higher maintenance expenditures. 4-stroke engines, on the other hand, require less regular maintenance and typically last longer.
-
Power Delivery
2-stroke engines typically have fewer moving parts and a more straightforward design. A more abrupt power delivery may come from this, which may be preferable in some situations, like racing or off-road riding. On the other hand, 4-stroke engines often provide power more steadily and smoothly, making them preferred for uses where a constant amount of power is required, such as a generator or water pump.
Conclusion
From vehicles to lawnmowers, internal combustion engines are crucial to many contemporary devices. The 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines are two of the most popular varieties of internal combustion engines. Although both kinds of engines transform fuel into energy, they do so in very different ways mechanically. When it comes to 2 stroke vs 4 stroke engines, both of them include pros and cons.
The fundamental distinctions between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines will be covered in this article.
-
Number of strokes
The stroke numbers necessary to complete a combustion cycle are the primary distinction between the two types of engines. The name of the engines is self-explanatory. The compression and the power stroke are the two strokes that make up a 2-stroke engine’s combustion cycle. In contrast, the combustion cycle in a 4-stroke engine is completed by four strokes: the intake, the compression, the power, and the exhaust.
-
Simplicity
Due to its simplicity, a 2-stroke engine is typically lighter, smaller, and less expensive to produce than a 4-stroke engine. Because of this, 2-stroke engines are widely used in products where weight and size are important considerations, such as chainsaws, mopeds, and some small boats. However, 2-stroke engines often use more fuel and pollute more than 4-stroke engines.
-
Fuel Efficiency
Regarding fuel efficiency in 2stroke vs 4stroke engines, 4-stroke outperforms its counterpart. The way 2-stroke engines deliver fuel to the combustion chamber contributes to their decreased fuel economy and more significant emissions. A 2-stroke engine’s combustion chamber receives the gasoline and oil mixture through ports in the cylinder wall. The emission of unburned fuel and contaminants can occur as a result of this process’ potential for incomplete combustion.
On the other hand, the moving elements of 4-stroke engines are lubricated by a separate oil system, which enables a cleaner combustion process. A 4-stroke engine’s intake stroke enables a more thorough mixing of fuel and air, which enhances the combustion process and increases fuel economy.
-
Maintenance Frequency
The need for maintenance is another significant distinction between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. Due to their straightforward construction and requirement to mix oil and gasoline, 2-stroke engines need maintenance more frequently. Throughout the engine’s lifetime, this may lead to higher maintenance expenditures. 4-stroke engines, on the other hand, require less regular maintenance and typically last longer.
-
Power Delivery
2-stroke engines typically have fewer moving parts and a more straightforward design. A more abrupt power delivery may come from this, which may be preferable in some situations, like racing or off-road riding. On the other hand, 4-stroke engines often provide power more steadily and smoothly, making them preferred for uses where a constant amount of power is required, such as a generator or water pump.
Conclusion
There is no clear winner in 2stroke vs 4stroke engines. Both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines offer benefits and drawbacks. Due to their simplicity and compactness, 2-stroke engines are appropriate for situations where weight and size are important factors. Nevertheless, 4-stroke engines often use less fuel and last longer. To determine which type of engine is best for a given application, it is crucial to consider the demands of that application.
Nevertheless, 4-stroke engines often use less fuel and last longer. To determine which type of engine is best for a given application, it is crucial to consider the demands of that application.